A previous article considered the basic requirements for externally illuminated exit signs. This article considers internally illuminated signs, where the sign is illuminated from behind the sign.
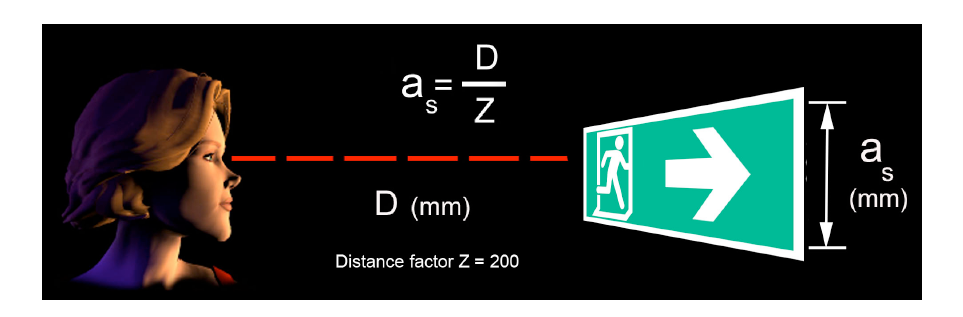
As discussed in the previous article Approved Document B only refers to the signs and signals regulations which does not give any guidance regarding the size of signs. The standard for the size of signs is given in three codes BS 5266: Part 1 (A code for escape lighting), BS 5499: Part 4 and BS 5266: Part 7 (Emergency lighting applications). All three codes give the same formula which is used for both externally illuminated signs and internally illuminated signs, except that a value known as the ‘Distance factor’ is specified for internally illuminated signs as 200, whereas for externally illuminated signs it is 100; representing the illumination by escape lighting.
What this effectively means is that internally illuminated signs can be 50% smaller than externally illuminated signs. This is because internally illuminated signs are regarded as being discernable at a greater distance.
The table below reproduced from BS 5266: Part 1 gives values for other levels of illumination and the corresponding distance factor. However a distance factor of 200 is the figure given in BS 5266: Part 7 for the escape lighting condition with internally illuminated signs and as the same light fitting is used for the non emergency condition the distance factor of 200 would also apply. Therefore the other values seem to be irrelevant except for Gaseous tritium (self powered) signs which need the reduced Distance factor of 50.
herefore for both normal lighting and emergency conditions a distance factor of 200 should be used. An example showing how the sign height is calculated is given below.
Where as = height of the sign
D = distance viewed
Z = distance factor from the table below (reproduced from BS 5266: Part 1)